The Gaming Blog
Introduction to Foot Neuropathy
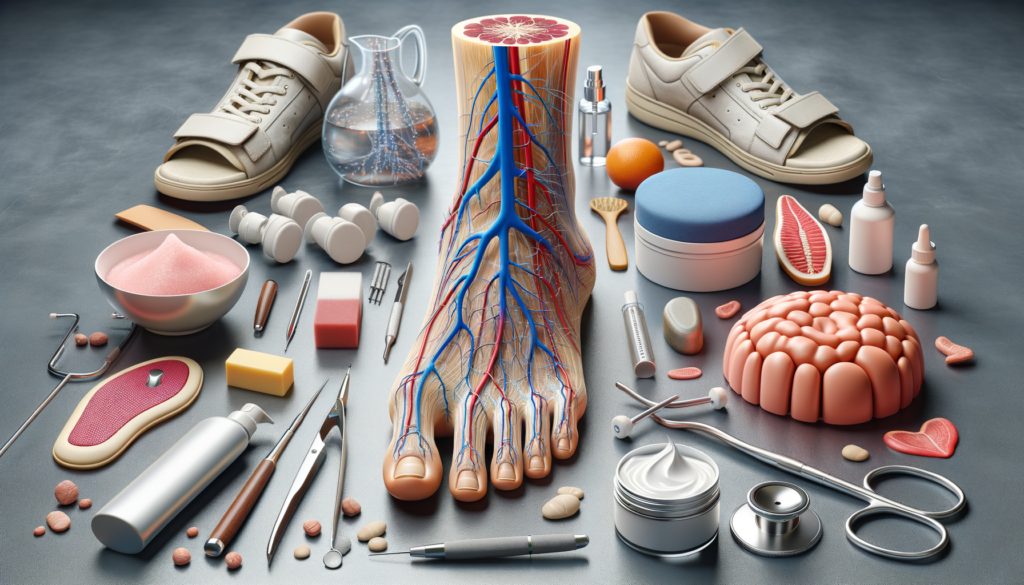
Foot neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage in the feet, is often linked to diabetes. This condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and even severe complications if not managed properly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for those affected by this condition. This article delves into various aspects of foot neuropathy, offering insights and practical advice for effective management.
Causes and Symptoms of Foot Neuropathy
Foot neuropathy primarily results from prolonged high blood sugar levels that damage the nerves over time. Other contributing factors include nerve injuries, infections, and exposure to toxins. Symptoms can vary significantly among individuals but often include:
- Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes.
- Tingling or burning sensations in the feet.
- Sharp pains or cramps.
- Increased sensitivity to touch.
Identifying these symptoms early is essential in preventing further complications. Regular check-ups and monitoring can help in managing the condition effectively.
Treatment Options for Foot Neuropathy
Treatment of foot neuropathy focuses on managing symptoms and preventing further nerve damage. Here are some common approaches:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-seizure drugs, and topical treatments can help alleviate symptoms.
- Physical therapy: Exercises can improve muscle strength and coordination.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can significantly impact blood sugar levels and overall nerve health.
Consulting with healthcare professionals to tailor a treatment plan suited to individual needs is highly recommended.
Diabetic Foot Care: Essential Practices
For individuals with diabetes, foot care is a critical component of overall health management. Proper diabetic foot care can prevent complications such as ulcers and infections. Key practices include:
- Regularly inspecting feet for cuts, blisters, or swelling.
- Wearing comfortable, well-fitted shoes to prevent injury.
- Keeping feet clean and dry to avoid fungal infections.
Incorporating these practices into daily routines can help maintain foot health and prevent severe complications.
Conclusion: Proactive Management for Better Outcomes
Managing foot neuropathy and diabetic foot care requires a proactive approach. By understanding the condition and implementing effective treatment and care strategies, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, combined with self-care practices, are key to managing symptoms and preventing complications. Embracing these strategies empowers individuals to take control of their health and well-being.