The Gaming Blog

Introduction to Diabetes and Its Management
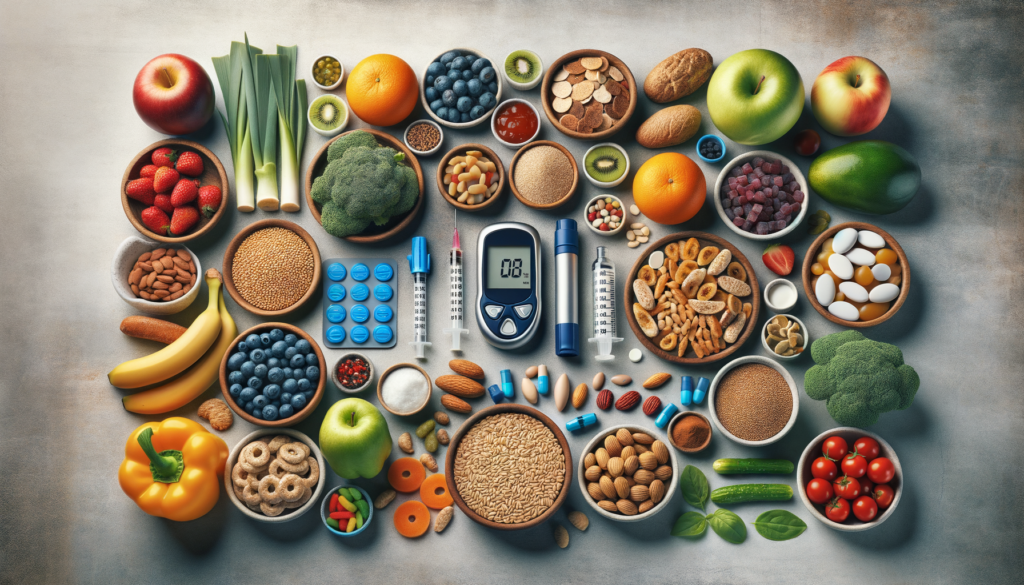
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions worldwide, characterized by high levels of sugar in the blood. Managing diabetes effectively is crucial to prevent complications and improve quality of life. Among the various types, type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent, often associated with lifestyle factors. Understanding the treatment options and dietary choices, such as low glycemic index foods, can significantly influence the management of this condition.
Type 2 Diabetes Treatment: A Comprehensive Approach
Type 2 diabetes management involves a multifaceted approach, combining medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Medications may include metformin or insulin therapy, tailored to individual needs. Lifestyle changes play a pivotal role, focusing on regular physical activity and healthy eating habits. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps in adjusting treatment plans effectively, ensuring optimal control over the condition.
Key components of managing type 2 diabetes include:
- Regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity and control weight.
- Healthy eating patterns focusing on balanced nutrition.
- Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels.
- Adherence to prescribed medications and regular consultations with healthcare providers.
These elements work together to maintain blood sugar levels within target ranges, reducing the risk of complications and improving overall health.
The Role of Low Glycemic Index Foods in Diabetes Management
Low glycemic index (GI) foods are integral to a diabetes-friendly diet. The glycemic index measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a low GI are digested and absorbed more slowly, leading to gradual increases in blood sugar. This is beneficial for individuals with diabetes, as it helps in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
Incorporating low GI foods into meals can help in managing diabetes effectively. Examples of such foods include:
- Whole grains like oats and barley.
- Legumes such as lentils and chickpeas.
- Non-starchy vegetables including broccoli and spinach.
- Fruits like apples and berries.
These foods not only aid in blood sugar control but also contribute to a balanced and nutritious diet, supporting overall health and well-being.
Comparing Dietary Strategies for Diabetes Control
When it comes to dietary strategies for diabetes management, there are various approaches one can consider. These include low carbohydrate diets, Mediterranean diets, and plant-based diets, each with unique benefits.
Low carbohydrate diets focus on reducing carb intake to minimize blood sugar spikes. The Mediterranean diet emphasizes healthy fats, lean proteins, and abundant fruits and vegetables, promoting heart health. Plant-based diets, rich in fiber and antioxidants, support weight management and improve insulin sensitivity.
Choosing the right dietary strategy depends on individual preferences, lifestyle, and health goals. Consulting with a healthcare provider or nutritionist can help in tailoring a plan that suits personal needs and enhances diabetes management.
Conclusion: Empowering Choices for Better Health
Managing diabetes, particularly type 2, requires a proactive approach involving effective treatment plans and informed dietary choices. By understanding the importance of low glycemic index foods and exploring various dietary strategies, individuals can make empowered decisions to control their diabetes. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals ensure that the management plan remains effective and aligned with health goals, ultimately leading to improved quality of life and reduced risk of complications.