The Gaming Blog
Introduction to Osteoporosis
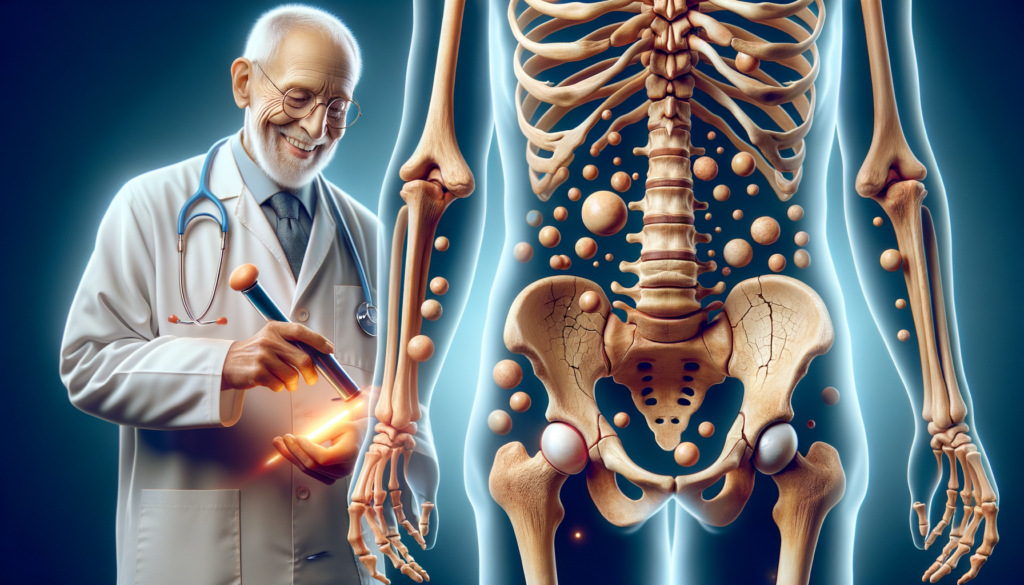
Osteoporosis is a chronic condition characterized by the weakening of bones, making them fragile and more susceptible to fractures. It affects millions of people worldwide, particularly postmenopausal women, but it can also occur in men and younger individuals. The condition develops silently over the years, often without symptoms until a fracture occurs. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and management options for osteoporosis is crucial for prevention and maintaining bone health.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of osteoporosis is influenced by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Key causes include hormonal changes, particularly the decrease in estrogen levels in women after menopause. Other risk factors include:
- Aging: Bone density naturally decreases with age.
- Family history: A family history of osteoporosis can increase risk.
- Low body weight: Individuals with lower body mass are at higher risk.
- Dietary factors: Low calcium and vitamin D intake can contribute to bone loss.
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones.
Understanding these factors can help in developing personalized strategies for prevention and management.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Osteoporosis is often called a “silent disease” because it progresses without noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs. Common fracture sites include the hip, spine, and wrist. Symptoms that may indicate osteoporosis include:
- Back pain, often caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra.
- Loss of height over time.
- A stooped posture.
- Fractures that occur more easily than expected.
Diagnosis is typically made using a bone density test, which measures the density of bones in various parts of the body. Early detection is essential for effective management and prevention of fractures.
Management and Treatment Options
Managing osteoporosis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and medical treatments. Key strategies include:
- Diet: Ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet and supplements.
- Exercise: Engaging in weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises to improve bone density and balance.
- Medication: Prescription medications may be recommended to slow bone loss and reduce fracture risk.
- Fall prevention: Implementing safety measures at home to prevent falls and fractures.
Working closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive management plan can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with osteoporosis.
Conclusion: Proactive Bone Health
Osteoporosis requires a proactive approach to maintain bone health and prevent fractures. By understanding the risk factors and symptoms, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk and manage the condition effectively. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and an active lifestyle are fundamental to maintaining strong bones. With the right strategies, it is possible to live a healthy and active life despite the challenges posed by osteoporosis.